SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF BILE DUCT CANCER
Bile duct cancer may not cause symptoms until it reaches an advanced stage. Some people may notice symptoms earlier such as -
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Itchy skin
- Tea-coloured urine and Pale stools
- Abdominal discomfort, pain or bloatedness
- Loss of appetite and weight or fatigue
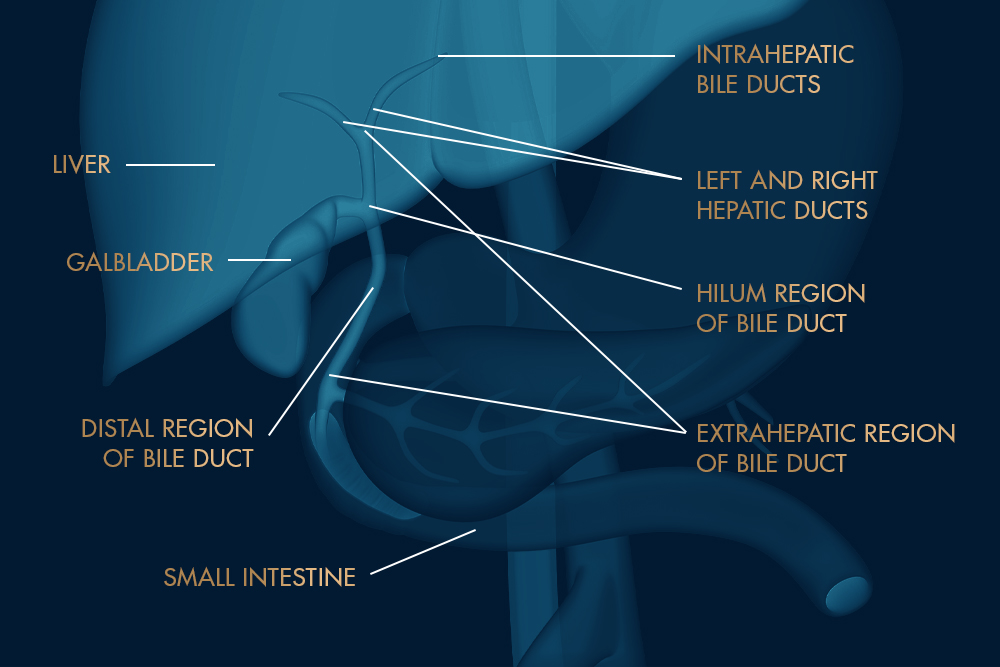
Types of bile duct cancer
These cancers can occur in the main bile duct within the liver (intrahepatic) or outside the liver (extrahepatic)
Risks Factors of Bile Duct Cancer
- Long-standing inflammation of the bile ducts e.g. liver parasite infections
- Chronic liver disease (Liver cirrhosis, Hepatitis B & C)
- Inflammatory conditions e.g. Primary sclerosing cholangitis, ulcerative colitis
- Bile duct cyst (Choledochal cyst)
- Drugs or toxins exposure
- Age ≥ 50; Obesity; Diabetes
How Is Bile Duct Cancer Diagnosed?
- A full medical history and clinical evaluation
- Blood Tests - Liver function tests and tumour markers
- Imaging – CT, MRI or PET scans - for assessment and staging
- Endoscopy (+/- ultrasound) or Cholangiography- for further evaluations and biopsy
- Combination of the above
Treatments for Bile Duct Cancer
Surgery is the preferred treatment for bile duct cancer that has not spread. This may involve removing the bile duct, portion of the liver and surrounding lymph nodes and involved organs.
Depending on the location and extent of the cancer, the following surgeries may be recommended.
- Liver Resection
- Bile duct resection & lymph node clearance
- Whipple surgery
- Liver transplant
Other treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy, in addition to surgery or for people when surgery is not appropriate.